Dear Readers,
In the previous posts, we covered the meaning and definition of key terms such as: Contract, Agreement and Consideration. Also, we discussed that an agreement without consideration is void. Please click on below link to read this post again
http://www.rkstrainings.com/what-do-we-mean-by-consideration/
Hence, one may wonder whether these are the only two necessary ingredients of a valid contract. In other words, if a contract satisfies these two requirements, whether, it is a legally binding and enforceable contract. The simple answer is NO. This is because there are few more things which are essential for a contract to be valid
All requirements, which make a contract legally enforceable, are called Essential Elements of a Valid Contract. An Agreement shall remain valid, if it contains all such compulsory ingredients. Otherwise, it becomes void and cannot be enforced
Indian Contract Act provides the followings as Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
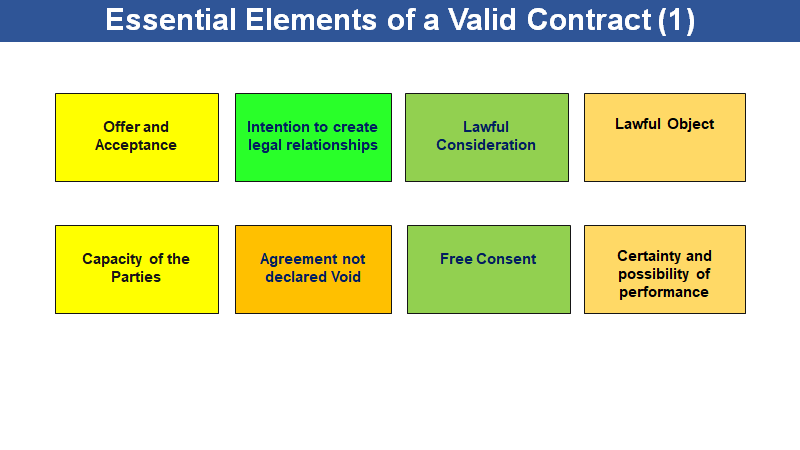
In this post, we shall be discussing 4 elements with brief explanation and examples. Balance 4 shall be discussed in next blog
Essential Elements of a valid Contract
A) Offer and Acceptance
This is the first and foremost requirements of a valid contract. Agreement said to arise between the parties when one party submits the offer and other one accept it. Provided the acceptance by other party is unconditional, absolute & unqualified and without any reservation or rider
In the event, other party gives conditional acceptance, the same constitute a counter offer rather than an agreement. As long as parties’ gives offer and counter offers, there is no agreement until they meet at mutually acceptable common point. We know this concept fully and deal with it daily while procuring goods or services from our vendors/contractors
B) Intention to create legal relations
This is the most fundamental requirement of a valid Contract. For a contract to be legally enforceable, parties to an agreement must have intention to create legal relationships. This means each party acknowledges that it is not only answerable to other party but also to the applicable law for its promises. Both parties understand that they are legally bound to fulfil their obligations as per agreed terms; otherwise, it may face legal consequences under the law.
However, if parties to an agreement do not intend to be bound legally, such an agreement is a mere MOU rather than a contract. Such agreements are void and cannot be enforceable by law. A document named as contract does not make it contract if it does not fulfil this requirement
C) Lawful Consideration
There must be some advantage or benefit moving from one party to another. Also, parties must be permitted under law to receive such advantage or benefit. As per section 25 of Indian Contract Act, agreement without consideration is void. Also, as per section 23, the agreement for which consideration is unlawful is void
In business transactions, one party provides the goods and other party make payment against the same. Similar one party provides services or executes work and other party makes the agreed payment. So, goods, services or work is consideration for one party and payment in lieu of the same is consideration for other party. All such considerations are lawful and permitted under law
However, law does not allow certain considerations. For example, if A & B agree that A will give a threat to C (A’s neighbour) against payment of Rs-10,000.00. Though money consideration available for A for carrying out the work for B, but, act of threat is neither legally permitted or nor morally correct. Hence, the consideration is illegal in nature and such contracts are VOID
D) Lawful Object
For a valid contract, the objective of the agreement should be lawful. If the purpose of an agreement is illegal, such agreement is void. As per section 23 of Indian Contract Act, the objective is said to lawful unless;
- It is forbidden by law or
- Is of such a nature that if permitted, it would defeat the provisions of any law; or is fraudulent; or
- Involves or implies, injury to a person or property of another; or
- The Court regards it as immoral, or opposed to public policy
=======================================================================
Disclaimer Statements: http://www.rkstrainings.com/disclaimer-statements/
Please read and accept disclaimer statements by clicking: http://www.rkstrainings.com/disclaimer-statements/


